blog
The 2026 Software Development Model: An AI Renaissance
By Mohan S Software development Digital transformation February 17, 2025

Software development trends in 2026 are being shaped less by incremental tooling and more by a fundamental shift in how software is conceived, built, and evolved. AI adoption has moved from experimentation to market gravity, compressing innovation cycles so aggressively that the time spent evaluating a new technology can exceed the period in which it remains relevant.
You may like to read: Top AI Trends
In 2026, the strategy of "watching and waiting" is no longer conservative; it is terminal. For the senior technologist, the focus has shifted from managing people who write code to managing the systems that generate it.
1. The SDLC is Dead: Welcome to the Continuous Loop
By 2026, AI has evolved from passive code assistants to autonomous agents capable of building entire features and managing the full Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC). This "Agentic Engineering" has compressed traditional month-long dev cycles into hours or days.
An Augment Code enterprise case study is one example of this shift: A project a CTO initially estimated would require eight months of human effort was shipped in just two weeks using agentic orchestration.
Multi-Agent Orchestration
The core enabler is coordinated multi-agent orchestration. Instead of a single assistant, teams now deploy specialized agents, coordinated by an orchestrator that decomposes high-level requirements into parallel workstreams such as feature development, testing, and review. These agents operate across isolated contexts, often using git worktrees, while standards like the Model Context Protocol (MCP) enable safe interaction with tools such as Jira, Slack, and internal systems.
The New Engineer: From Coder to Architect
The engineer’s job has evolved from coding to orchestrating autonomous agents: architecture, system design, and problem decomposition are human responsibilities, while AI performs implementation, testing, and much debugging.
Platforms like Devin, Cursor Composer, GitHub Copilot Workspace, and PlayCode Agent have reduced onboarding from weeks to hours and expanded developer scope across infra and security.
Still, although AI is involved in ~60% of engineering work, fully delegable tasks remain ~0–20%, making architectural clarity the primary bottleneck.
2. WebAssembly 3.0: Containers Stop Being the Bottleneck
By 2026, Wasm 3.0 has the browser to become the industry standard for cloud-native, edge, and server-side computing. It serves as a high-performance, secure, and language-agnostic foundation for modern architecture.
Key Technical Innovations
Wasm 3.0 closes the long-standing gap between web technologies and native performance by introducing a set of foundational capabilities rather than incremental optimizations.
The new Component Model enables true cross-language interoperability, allowing developers to compose Rust, Python, and Go modules into a single, seamless binary.
Memory64 removes the historical 4GB ceiling through 64-bit indexing, unlocking data-heavy AI and scientific workloads. With JS Promise Integration (JSPI), synchronous Wasm code can now interact cleanly with asynchronous Web APIs, dramatically simplifying the migration of legacy desktop applications to the web. Together with optimized built-ins such as JavaScript String Builtins and standardized exception handling (exnref), these changes eliminate much of the traditional glue code and significantly improve cross-platform reliability.
Wasm 3.0 is the "write once, run anywhere" solution for 2026. Serverless 2.0 allows near-instant startup speeds that have effectively eliminated the "cold start" issues of traditional containers. Edge & IoT adds lightweight, isolated runtime that allows high-performance apps (CAD, gaming) to run on low-power hardware at the network edge.
Wasm’s language-agnostic model (Rust, Go, C++, Python, .NET and more) democratizes high-performance development, and by 2026 frameworks that integrate Wasm with minimal tooling will hold a major competitive edge. According to current sources, Wasm 3.0 is no longer experimental: it’s a production-ready standard shaping how modern software is built for global scale and reliability.
3. GreenOps and the New "Inference Economics"
In 2026, Green Software and GreenOps have evolved from "nice-to-have" CSR initiatives into mandatory engineering requirements. Sustainability is now a core pillar of the SDLC, driven by the realization that carbon efficiency and cost efficiency are two sides of the same coin.
The GreenOps Framework embeds environmental accountability into operations. FinOps and GreenOps converge: running heavy AI workloads in renewable “green windows” can cut costs and emissions by about 50%. SCI (Software Carbon Intensity, ISO/IEC 21031) standardizes emissions per unit of work. Carbon-aware scheduling defers noncritical tasks until local grids have renewable surplus. Green coding best practices - energy-efficient languages (Rust), lightweight frontends (SvelteKit), serverless and container pooling to eliminate idle compute, model right-sizing with Small Language Models, and data minimization, further reduce compute, network, and storage energy use.
Cloud & AI to the Rescue
Visibility and accountability. Developers can now see the real-time carbon impact of their code, measured in grams of CO₂, directly within CI/CD pipelines, making sustainability a first-class engineering metric rather than a quarterly report. Decarbonization at scale is being accelerated by AI and IoT, which optimize logistics and manufacturing and could reduce global emissions by up to 32 gigatons by 2050. Meanwhile, net-zero infrastructure is becoming viable as the major cloud providers move toward 100% renewable energy, supplying the green foundation required for genuinely sustainable software systems.
4. Platform Engineering & IDPs
Platform engineering in 2026 isn't just about tools; it’s an operating model designed to industrialize software delivery so that "artisan" manual work is replaced by scalable, automated systems.
The Core Concept: "Golden Paths"
Platform engineering’s greatest contribution is the Golden Path which is a standardized, pre-approved workflow that makes the "right way" the "easy way."
The Internal Developer Platform (IDP) makes self-service real: developers provision databases, spin up staging, or instrument SLOs with a single click, with no Jira ticket needed. By abstracting Kubernetes and cloud-native complexity, it reduces cognitive load and keeps senior engineers from becoming the “human glue” of infrastructure. As the central control plane, the IDP enforces governance automatically. Security, FinOps, and GreenOps policies apply to every deployment, human or AI.
The 2026 Evolution: Agentic Engineering Platforms
The most significant shift this year is the transformation of IDPs into Agentic Engineering Platforms:
The Internal Developer Platform now treats AI as a first-class user. Through Agent Skill Wrapping, the platform exposes APIs and context so agents can autonomously handle PR reviews, resolve tickets, and perform self-healing. Centralized Context Lakes feed real-time engineering data to agents, keeping actions accurate and inside organizational guardrails. The IDP UI supports transparent hand-offs between human architects and autonomous agents, making collaboration clear and auditable.
Mature IDPs drive business growth by slashing onboarding and release times through automation and self-service. This creates a competitive edge by increasing developer retention and ensuring "by-default" compliance with global regulations.
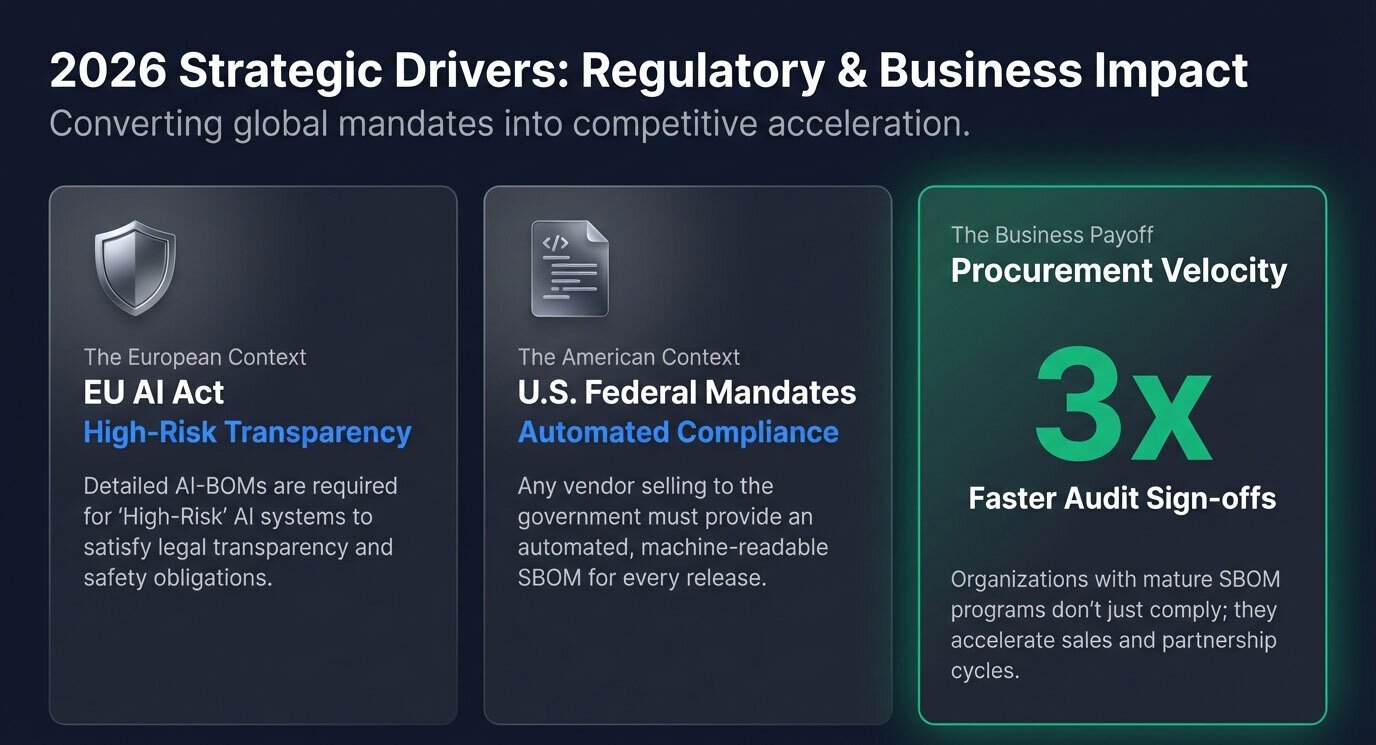
5. From SBOM to AIBOM
The most significant shift in 2026 is the expansion of the SBOM into the AI Bill of Materials (AI-BOM). Traditional lists of code libraries are no longer sufficient for systems that rely on non-deterministic models:
Model Provenance: Tracks the lineage of an AI model, from the base foundation model to specific fine-tuning adapters and versioned weights.
Dataset Transparency: Catalogs the training data, ensuring compliance with intellectual property laws and documenting potential biases or "poisoned" data risks.
Stochastic Tracking: Unlike static code, AI-BOMs track "dynamic dependencies" like prompt templates and orchestration frameworks (e.g., LangChain or Semantic Kernel).
The SDLC Handshake: The "Digital Notary"
The "Handshake" is the process where the code proves its identity to the infrastructure. In 2026, this is powered by Continuous Attestation.
Zero-Trust Enforcement: In 2026, production environments are "locked." The only way a container can run is if it presents a cryptographic signature that matches the SBOM/AIBOM generated during the build. No signature = no execution.
The "Shift Down" Effect: This is the ultimate "Shift Down." Instead of making developers manually check for compliance (Shift Left), the platform's infrastructure handles the handshake automatically.
Risks & Maneuvers Needed As We Dive In
According to the Zscaler ThreatLabz 2025 Ransomware Report, the volume of exfiltrated data rose by 92.7% as threat actors began weaponizing generative AI to analyze stolen data for maximum extortion leverage and to debug malware code. This industrialization of AI-powered attacks has effectively vanished the barrier to entry for launching sophisticated, targeted campaigns at scale.
Organizations face exponential risk from "Shadow AI," where unauthorized agents operate without standard security governance or oversight
Organizations adopt security-first architectures, embedding protection as code from day one through Zero Trust, automated SBOMs, and AI-driven defense.
Agentic security and evaluation gates continuously verify users, components, and AI-generated code, shrinking breach impact and enforcing regulatory and architectural compliance.
The Courage to Redesign
The Renaissance of Autonomy is not about layering AI onto legacy processes; it is about the courage to rebuild the operating model from the ground up. The organizations thriving in 2026 are those that have transitioned from being "code-centric" to "orchestration-centric." They recognize that in an era of multiplicative innovation, speed is a byproduct of discipline.
As you evaluate your roadmap for the coming year, the question is no longer how to enhance what you have. Instead, ask whether incremental improvement is enough, or whether what comes next demands a fundamental rebuild.


